Publish your data on the BIG IoT marketplace
When building IoT systems, it is often useful to have access to data from the outside world to amend the information your sensors give you. For example, indoor temperature and energy usage measurements will be a lot more useful if there is information on the outside weather to correlate with.
Thanks to the open data movement, there are many data sets available. However, many of these are hard to discover or available in obscure formats.
The BIG IoT marketplace
BIG IoT is an EU-funded research project to make datasets easier to share and discover between organizations. With it there is a common semantic standard for how datasets are served, and a centralized marketplace for discovering and subscribing to data offerings.
- For data providers this means they can focus on providing correct information, and let the marketplace handle API tokens, discoverability, and — for commercial datasets — billing
- For data consumers there is a single place and a single API to access multiple datasets. No need to handle different Terms of Usage or different API conventions
As an example, if you’re building a car navigation application, you can use BIG IoT to get access to multiple providers of routing services, traffic delay information, or parking spots. If a dataset comes online in a new city, it’ll automatically work with your application. No need for contract negotiations, just a query to find matching providers on-demand.
Flowhub and BIG IoT
Last summer Flowhub was one of the companies accepted into the BIG IoT first open call. In it, we received some funding to make it possible to publish data from Flowhub and NoFlo on the marketplace. In this video I’m talking about the project:
In the project we built three things:
- BIG IoT JavaScript library – a Node.js library for publishing datasets in the BIG IoT marketplace
- Flowhub BIG IoT bridge – a set of NoFlo components for creating BIG IoT providers
- Deutsche Bahn and Cologne parking offerings – a set of live examples of integrating existing IoT datasets with the marketplace using Flowhub
Creating a data provider
While it is easy enough to use the BIG IoT Java library to publish datasets, the Flowhub integration we built it makes it even easier. You need your data source available on a message queue, a web API, or maybe a timeseries database. And then you need NoFlo and the flowhub-bigiot-bridge library.
The basic building block is the Provider component. This creates a Node.js application server to serve your datasets, and registers them to the BIG IoT marketplace.
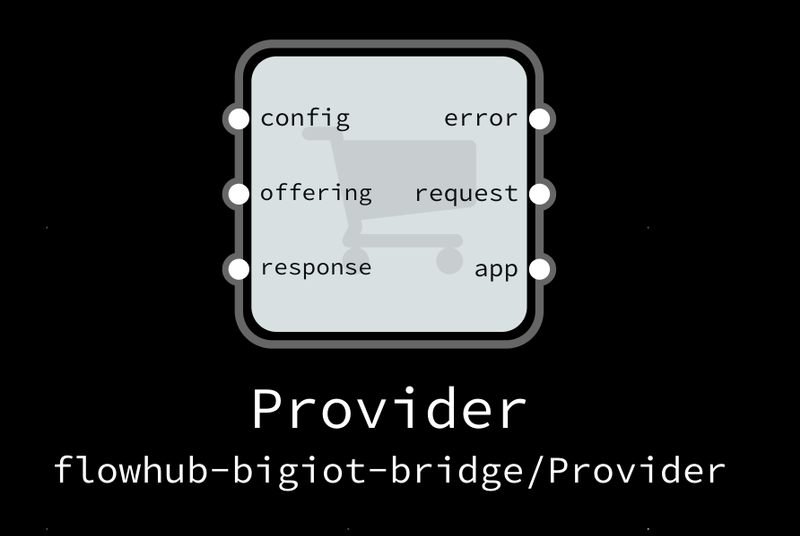
What you need to do is to describe your data offering. For this, you can use the CreateOffering component. You can use IIPs to categorize the data, and then a set of CreateDatatype components to describe the input and output structure your offering uses.
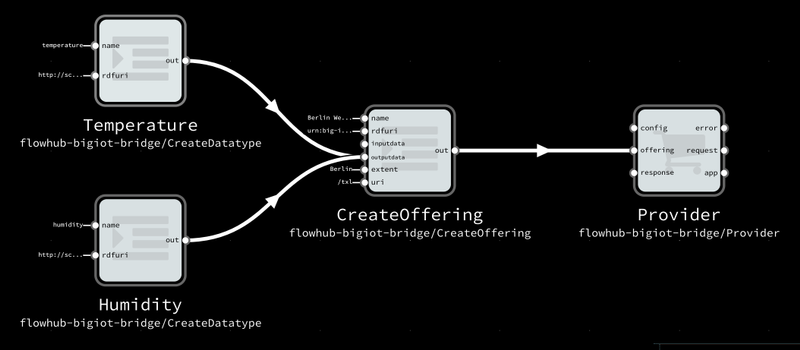
Finally, the request and response ports of the Provider need to be hooked to your data source. The request outport will send packets with whatever input data your subscribers provided, and you need to send the resulting output data to the response port.
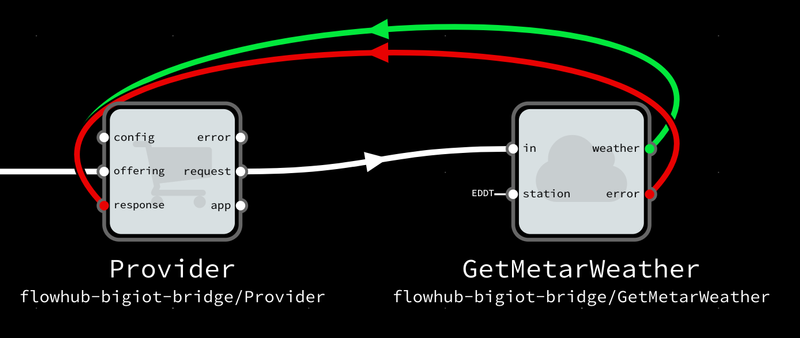
For real-world deployment, the Flowhub BIG IoT bridge repository also includes examples on how to test your offerings, and how to build and deploy them with Docker.
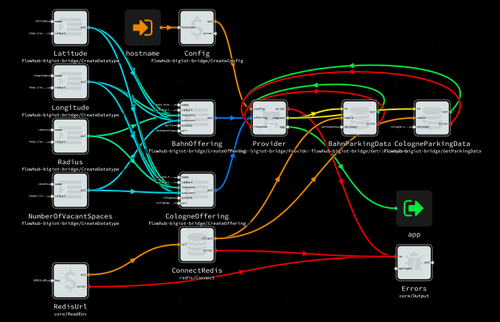
Here’s how a full setup with two different parking datasets looks like:
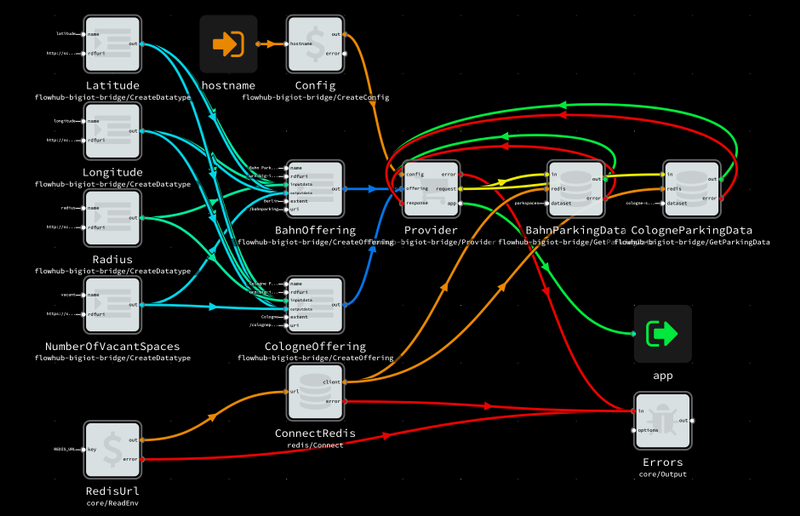
If you’re participating in the Bosch Connected World hackathon in Berlin next week, we’ll be there with the BIG IoT team to help projects to utilize the BIG IoT datasets.
This project has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program under grant agreement No 688038.